Post-fairness: Cross-task Adversarial Attack-based Instance Debiasing for Deactivating Spurious Correlations
Introduction
Neural networks often learn to make predictions that rely on social attributes like gender and race, which causes the model to be social biased. While previous work tackles this issue with training an unbiased model, but a stronger and common requirement in practice is a more challenging setting where model weights is unchangeable. In this paper, we propose a post-processing debiasing framework, and explore new ideas for achieving algorithm fairness. Our observations show that the biased model learn the bias feature and make biased decisions based on it. We propose an instance debiasing method based on adversarial attacks to remove the information in the test sample that will activate the bias feature of the model, and require that the features of the new instance deactivate model's biased decision-making relus, so that the model only makes predictions based on the target feature. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method in laboratory scenarios and real applications.
We summarize our main contributions as follows:
- We are the first to propose debiasing through instance transformation. Compared with pre-processing and intermediate processing, our method does not need to modify the model, as a lightweight plug-in to debias the biased model. Our method can also be compatibly used with pre and in-processing at the same time to enhanced debiasing effect. Compared with other post-processing methods, we can make great use of the target feature-based decision rules in the model to achieve debiasing and ensure accuracy on each instance, instead of transformation the prediction distribution to ensure fairness.
- Under the framework of instance transformation, we explored a function of adversarial attack: As a tool for sample generation, unbiased instances are generated by transforming the original image to remove bias feature.
Motivation
Not all results are based on task-irrelevant features in the input:

Fig.1 Model bias v.s. The level difficulty of the bias attribute recognition. Model bias of test samples with different levels in the classification of bias attributes.
The observation is "Not all results are based on task-irrelevant features in the input."" Instead, when the bias attribute of the test sample is difficult to recognition, the unfair target model will output fair results. Therefore, We obtain a direct idea: We can hide the bias information in the sample to make the model output from unfair to fair. Based on our above research, we consider that we can use adversarial attack to manipulate image with the target of removing bias information.
Regular adversarial attack can’t cross task

Fig.2 The debiaisng performance for different target model.
When we use adversarial attack achieve instance debiasing, the debiasing performance is not enough and far from our debiasing goal. But we only use the Natural Unbiased Instance to test, the model bias is much lower than the model bias obtained by using the entire test set and achieve excellent debiasing performance.
Analysis Framework
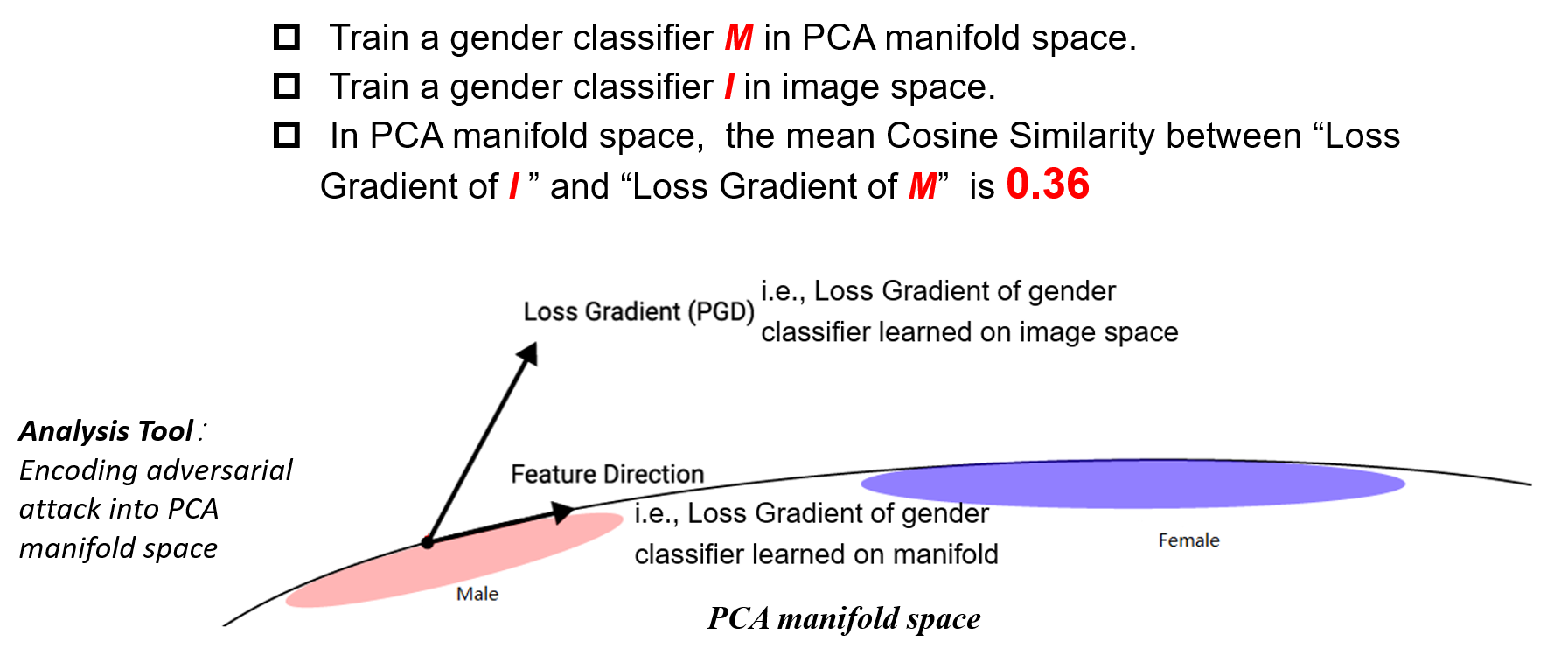
Fig.3 Take a closer look at the different between adversarial attack and Natural Unbiased Instanse by using manifold space as analysis tool.
Based on PCA manifold space, we can observe the relation between adversarial attack direction and manifold feature direction. We use the mean Cosine Similarity to measured, and observed that the mean Cosine Similarity between “Loss Gradient of I ” and “Loss Gradient of M” is 0.36. This low Cosine Similarity means The direction of adversarial attack isn’t feature direction,and this leads to underperform debiaisng.
Proposed Method

Fig.4 Illustration of the training process of the Post-fairness model.
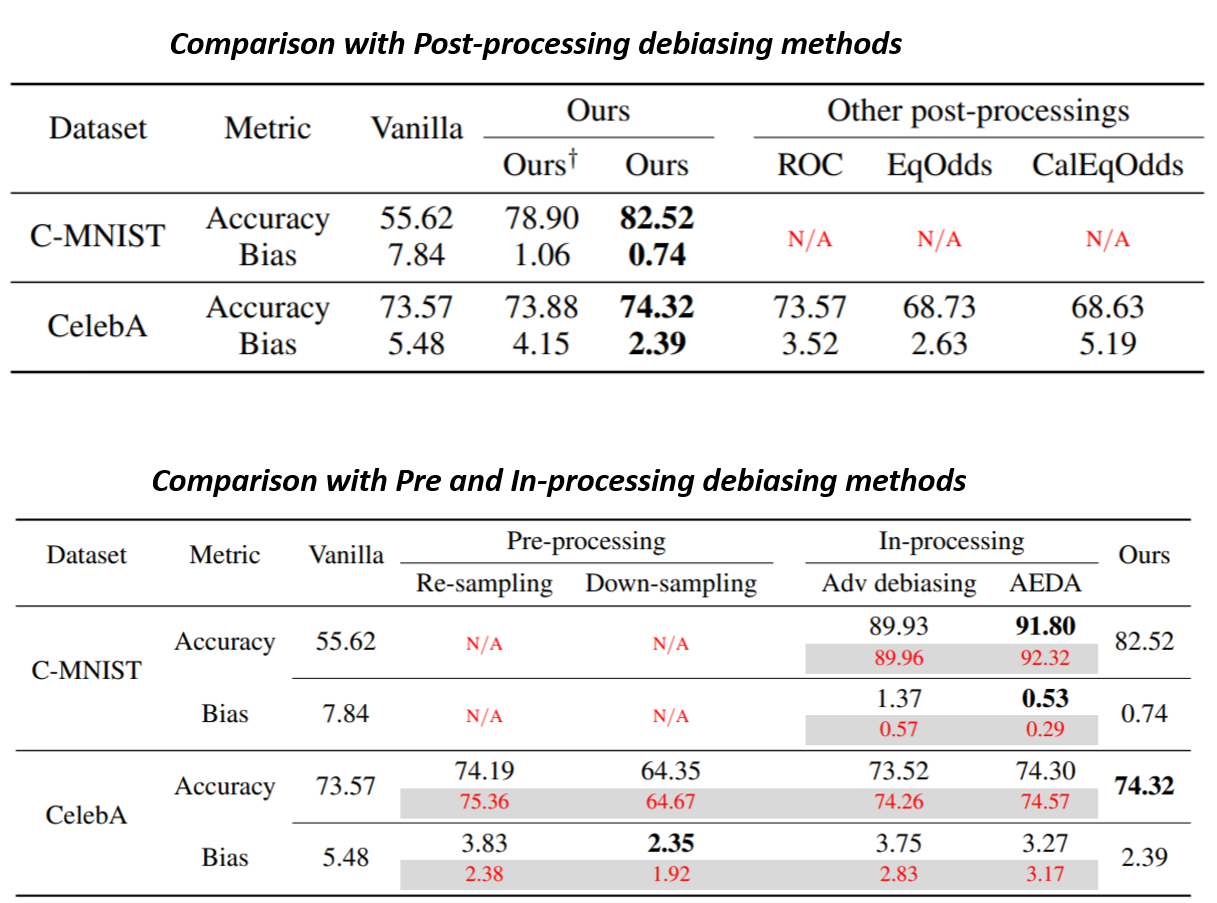
Debiasing Evaluation
Real-world application does not allow to modify model for debiasing, the only available debiasing method is the post-processing. We compare the performance of our algorithm with three typical post-processing debiasing algorithms. In laboratory scenarios, the debiasing algorithms can access to the data preparation and training stage to retrain model. To evaluate the effectiveness, we consider several typical pre and in-processing debiasing solutions. We evaluated the proposed AEDA solution on both simulated and real-world bias scenarios, all experimental results in evaluation support that Post-fairness successfully obtained the unbiased result in the biased model without modifying the original model.