Robust CAPTCHAs towards Malicious OCR
Introduction
Turing test was originally proposed to examine whether machine’s behavior is indistinguishable from a human. The most popular and practical Turing test is CAPTCHA, which is to discriminate algorithm from human by offering recognitionalike questions. The recent development of deep learning has significantly advanced the capability of algorithm in solving CAPTCHA questions, forcing CAPTCHA designers to increase question complexity. Instead of designing questions difficult for both algorithm and human, this study attempts to employ the limitations of algorithm to design robust CAPTCHA questions easily solvable to human. Specifically, our data analysis observes that human and algorithm demonstrates different vulnerability to visual distortions: adversarial perturbation is significantly annoying to algorithm yet friendly to human. We are motivated to employ adversarially perturbed images for robust CAPTCHA design in the context of character-based questions. Four modules of multi-target attack, ensemble adversarial training, image preprocessing differentiable approximation, and expectation are proposed to address the characteristics of character-based CAPTCHA cracking. Qualitative and quantitative experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed solution. We hope this study can lead to the discussions around adversarial attack/defense in CAPTCHA design and also inspire the future attempts in employing algorithm limitation for practical usage.
In summary, the contributions of this study are two-fold:
- We have discovered the different vulnerability between human and algorithm on visual distortions. Based on the observations, adversarial perturbation is employed to improve the robustness of character-based CAPTCHA.
- Corresponding to the characteristics of typical OCR cracking solutions, we proposed a novel methodology addressing issues including sequential recognition, indifferentiable image preprocessing, stochastic image transformation and black-box cracking.
Framework
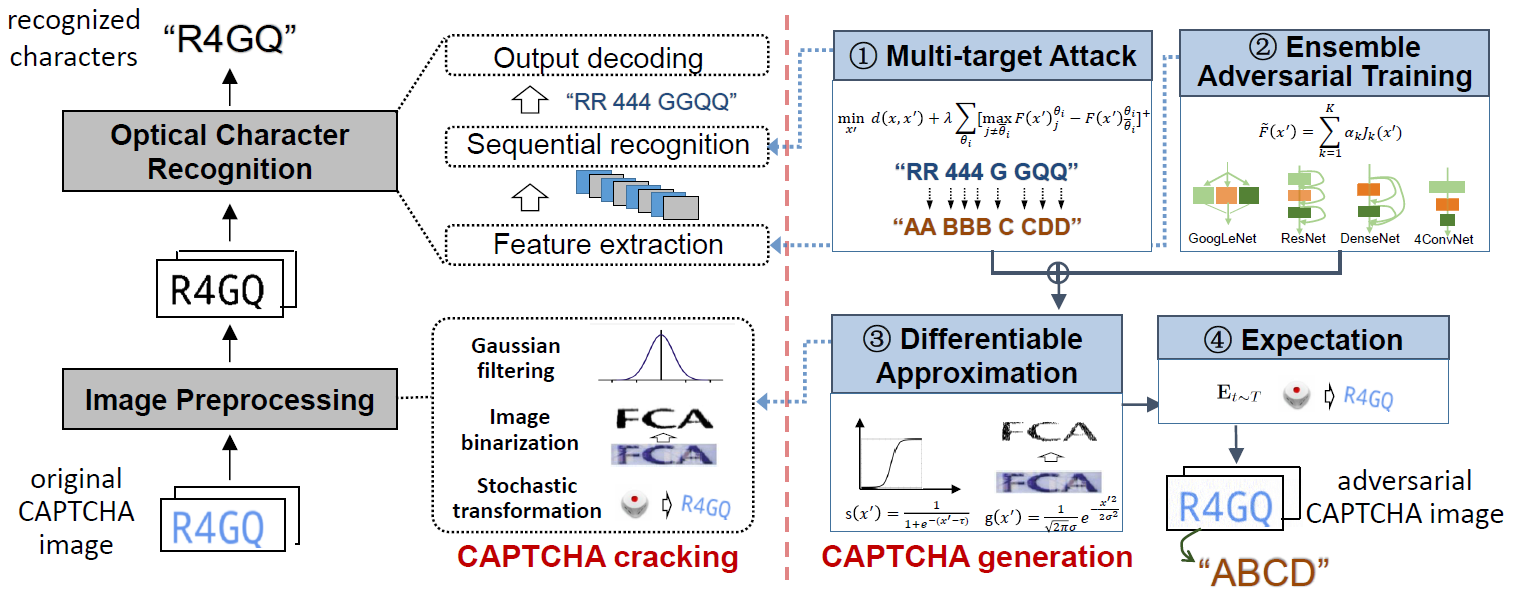
Fig.1 The proposed robust CAPTCHA designing framework. The left represents the process of CAPTCHA cracking, including sequential recognition, feature extraction, image binarization (Gaussian filtering) and stochastic transformation. The right represents our solution of CAPTCHA generation, including the corresponding multi-target attack, ensemble adversarial training, differentiable approximation and expectation, respectively.
The framework is shown on the Figure 1, the left shows that typical cracking of character-based CAPTCHA consists of two stages as image preprocessing and OCR. The above data analysis has demonstrated that image preprocessing has the effect of distortion removal, making it not possible to straightforwardly employ adversarial perturbation for robust CAPTCHA design. In addition to the image preprocessing stage, the OCR stage also possesses characteristics obstructing CAPTCHA:
(1)sequential recognition, disabling the traditional single character-oriented adversarial perturbation;
(2)black-box crack, making it ineffective to attack one specific OCR model. To address the above characteristics of CAPTCHA cracking, our proposed CAPTCHA.
Results
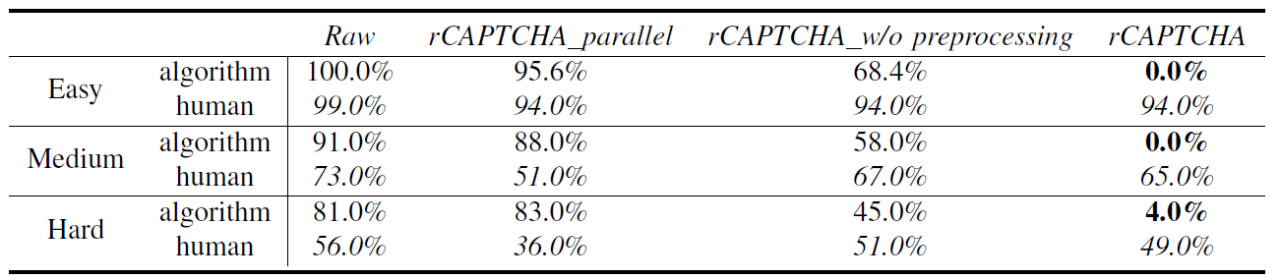
Table.1 The recognition of CAPTCHAs with different levels of complexity is performed in different settings. The results of the algorithm are obtained after Gaussian filtering and image binarization.
To compare the performance of the proposed robust CAPTCHA (rCAPTCHA) designing method, we report the recognition accuracies of state-of-the-art cracking solution under the following settings:
Raw: the original CAPTCHA images without adding adversarial perturbations;
rCAPTCHA parallel: the proposed solution to generated adversarial images, expect that the sequential recognition sequential recognition sub-module of OCR is replaced by 4 parallel recognition networks (each realized by one fully-connected layer) to address one character’s recognition;
rCAPTCHA w/o preprocessing: the proposed solution to generated adversarial images, but without considering the image preprocessing stages;
rCAPTCHA:the proposed solution to generated adversarial images, considering both sequential recognition and image preprocessing operations.
To examine the application scope of the proposed CAPTCHA generation methods, we conducted experiments on the CAPTCHAs with three levels of complexities: easy, medium, hard. For each of the settings, we selected/generated 500 CAPTCHA images for testing, and summarize the derived average recognition accuracy in Table 1. Experimental observations include:
(1) By adding adversarial perturbations, the right 3 columns consistently obtain lower accuracies than the first column, showing the usability of employing adversarial perturbations in resisting CAPTCHA cracking.
(2) Without considering the sequential recognition or image preprocessing characteristics, the resisting effect of rCAPTCHA parallel and rCAPTCHA w/o preprocessing is not as obvious as that of rCAPCHA. This validates the necessity of multi-target attack and differentiable approximation modules.
(3) Regarding CAPTCHAs with different complexities, we observed consistent phenomenon among the four settings, demonstrating the wide application scope of the proposed CAPTCHA generation method.
